Understanding the Definitions of Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity
Ionization energy is related with making cations from neutral atoms and electron affinity is related with making. Mol ionization energy 9470 kJ mol heat of fusion KJ 277 mol You may find additional useful data in.

8 3c Understanding The Definitions Of Ionization Energy And Electron Affinity Youtube
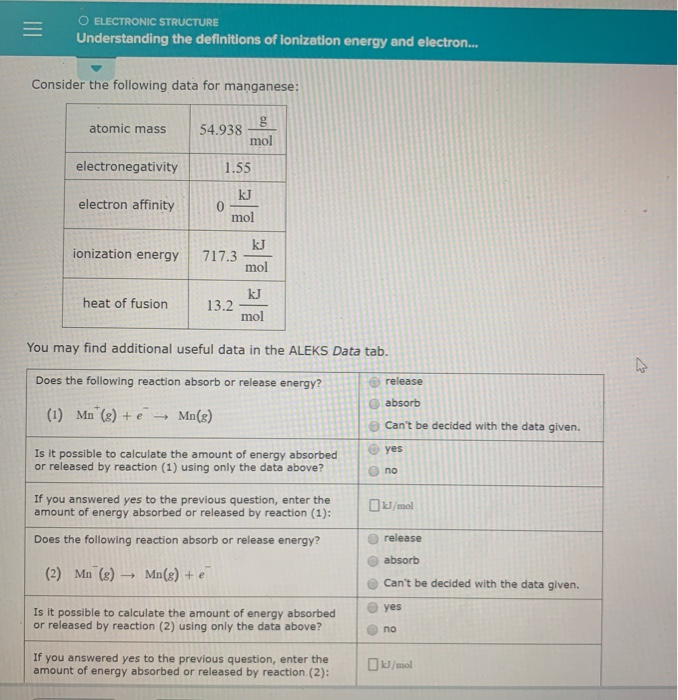
O ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE Understanding the definitions of ionization energy and electron.
. Therefore increased energy of ionization. Can anyone explain these to me in normal English please. This is a loose connection not a real causation for one or the other.
So the more negative the electron affinity the more favourable the electron addition process is. It is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. Electron affinity reflects the ability of an atom to accept an electron.
Understanding the definitions of energy and electron affinity Problem. The reaction that occurs when an atom takes an electron may be represented as. Similarly electron affinity decreases from top to bottom down the table just as ionization energy does.
For alkaline earth metals increased energy is required to fully ionize due to extra pull on second electron after the first escapes. A reaction in which a neutral atom loses an outer electron e- on the right side of the equation is called an ionization reaction. The change in energy in kJmole of a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous phase when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion.
Electron affinity Electronegativity Ionization energy 1. Atomic mass 74922 mol electronegativity 218 electron affinity kJ 78. People come across two terms viz electronegativity and electron affinity while dealing with bonds and atoms.
Electro Negativity Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity. X e X energy. Electron affinity is an atoms likelihood of gaining an electron.
Atoms with stronger effective nuclear charge have greater electron affinity. The process by which the first ionization energy of hydrogen is measured would be represented by the following equation. Electron affinity and ionization energy are two chemical terms used to describe the behavior of electrons and atom quantitatively.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Heat of fusion 197 k mol You may find additional useful data in the ALEKS Data tab. The electron affinity is the potential energy change of the atom when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom to form a negative ion.
Consider the following data for potassium. In chemistry and atomic physics the electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as. Since atoms with high ionization energies are less prone to losing electrons this usually means that these elements are more electronegative and are instead prone to accepting electrons.
I am having a hard time understanding these concepts from the definitions given in the book and from my teacher. Does the following reaction absorb or release energy. In the year 1932 Linus Pauling proposed the concept of electronegativity.
Ionization energy is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from a neutral atom. Electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy liberated when a. Ionization reactions always absorb energy called the ionization energy IE.
Understanding the definitions of ionization energy and electron. For electron affinity since the nucleus has such a strong pull by the third electron any element with more than three valence electrons is going to want to take electrons rather than lose them due. By definition the first ionization energy of an element is the energy needed to remove the outermost or highest energy electron from a neutral atom in the gas phase.
Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity Section 74-75 Objectives Examine periodic trends in ionization energy Examine periodic trends in electron affinity Key Terms Ionization energy Electron Affinity Ionization Energy Ease at which electrons can be removed from an atom or ion First ionization energy I1 is the energy required to remove the first electron from neutral atom. Consider the following data for arsenic. Atomic mass g 39098 mol electronegativity 082 electron affinity kJ 484 mol ionization energy KJ 4188 mol kJ heat of fusion 233 mol You may find additional useful data in the ALEKS Data tab.
Atomic mass 26982 B mol electronegativity 161 kJ 425 mol electron affinity ionization energy 5775 mol heat of fusion 107 mol You may find additional useful data in the ALEKS Data tab. Lorenzo Consider the following data for antimony. The electron affinity of an atom increases along the periods on the table just as ionization energy also increases.
The energy released when an electron is added to a gaseous atom which is in its ground state to form a gaseous negative ion is defined as the first electron affinity. The main difference between electron affinity and ionization energy is that electron affinity gives the amount of energy released when an atom gains an electron whereas ionization energy is the amount of energy required to remove an. Electronegativity is defined as a chemical property which decides the propensity of an atom to attract an electron.
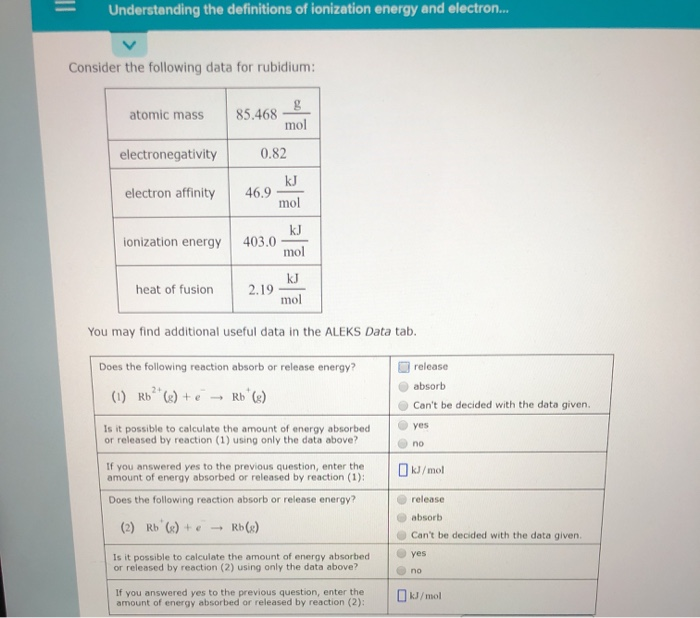
What is the difference between Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity. O ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE Understanding the definitions of ionization energy and electron. Understanding the definitions of ionization energy and electron.
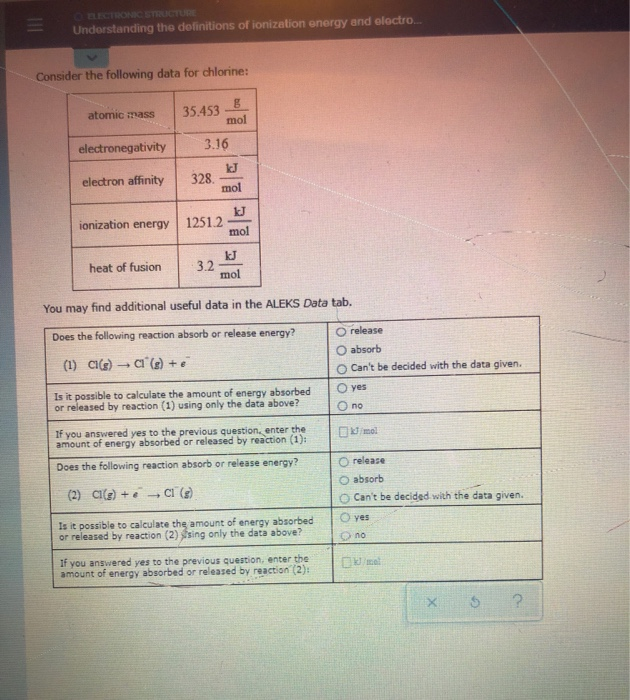
Not all elements form stable negative ions in which case the electron affinity is zero or even positive. The cause of the decrease in both electron affinity and ionization energy is the same as well the shielding effect. Consider the following data for tin.
E O ELECTRONC STRUCTURE Understanding the definitions of ionization energy and electron Consider the following data for aluminum. H g H g e -. Atomic mass 12176 mol electronegativity 205 electron affinity 1032 ole mol ionization energy 834.
Electron affinity is the amount of energy released when electron is added to an atom. Atomic mass 11871 g mol electronegativity 196 electron affinity 1073 kJ mol ionization energy kJ 7086 mol heat of fusion KJ 70 mol You may find additional useful data in the ALEKS Data tab.
Solved Understanding The Definitions Of Ionization Energy Chegg Com

Solved O Electronic Structure Understanding The Definitions Chegg Com
Solved Understanding The Definitions Of Ionization Energy Chegg Com
No comments for "Understanding the Definitions of Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity"
Post a Comment